简介
从模拟输入重复读取,计算运行平均值 并将其打印到计算机上。在数组中保留十个读数 不断平均他们,使值更平滑。
硬件要求
- Arduino or Genuino 开发板
- 10kΩ 电位计
电路
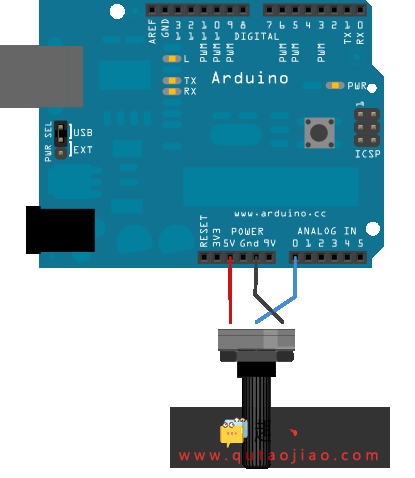
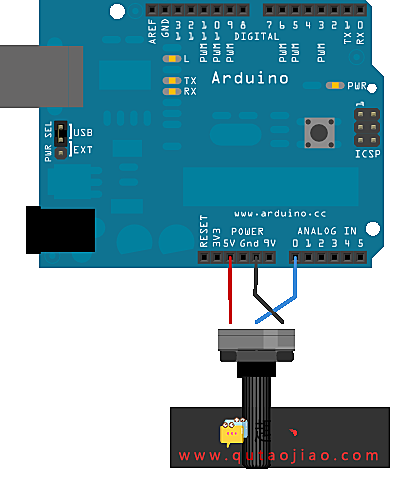
把电位计的一个引脚连接到5V,中间引脚连接到模拟引脚A0,最后的引脚连接到地。
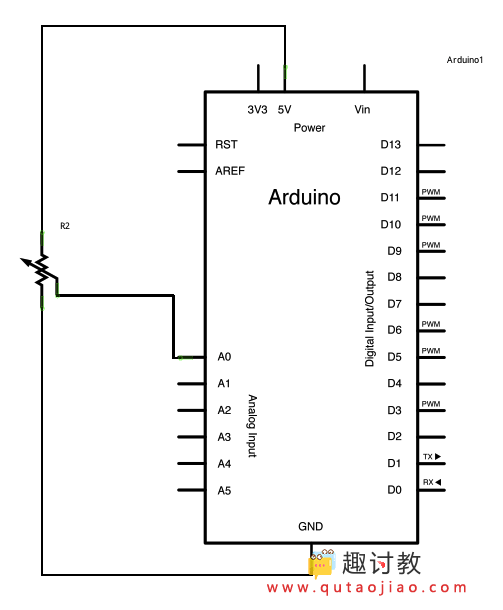
原理图
样例代码
下面的代码顺序保存10个模拟引脚的读取值,一个接一个放进一个数组里。每一次有新的值,把所有值加起来,然后取平均值,把这个平均值用作平滑输出的数据。因为这种平均每次加一个新的值到数组里(好过一次等够10个新值),分析运行的均值之间并没有滞后时间。
改变数组的大小,通过改变 numReadings 为一个更大的值将会使保存数据变得比之前平滑。
// Define the number of samples to keep track of. The higher the number,
// the more the readings will be smoothed, but the slower the output will
// respond to the input. Using a constant rather than a normal variable lets
// use this value to determine the size of the readings array.
const int numReadings = 10;
int readings[numReadings]; // the readings from the analog input
int readIndex = 0; // the index of the current reading
int total = 0; // the running total
int average = 0; // the average
int inputPin = A0;
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication with computer:
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize all the readings to 0:
for (int thisReading = 0; thisReading < numReadings; thisReading++) {
readings[thisReading] = 0;
}
}
void loop() {
// subtract the last reading:
total = total - readings[readIndex];
// read from the sensor:
readings[readIndex] = analogRead(inputPin);
// add the reading to the total:
total = total + readings[readIndex];
// advance to the next position in the array:
readIndex = readIndex + 1;
// if we're at the end of the array...
if (readIndex >= numReadings) {
// ...wrap around to the beginning:
readIndex = 0;
}
// calculate the average:
average = total / numReadings;
// send it to the computer as ASCII digits
Serial.println(average);
delay(1); // delay in between reads for stability
}