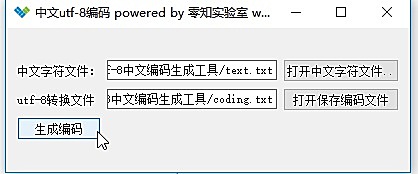
释放双眼,带上耳机,听听看~!
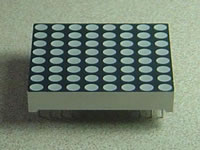
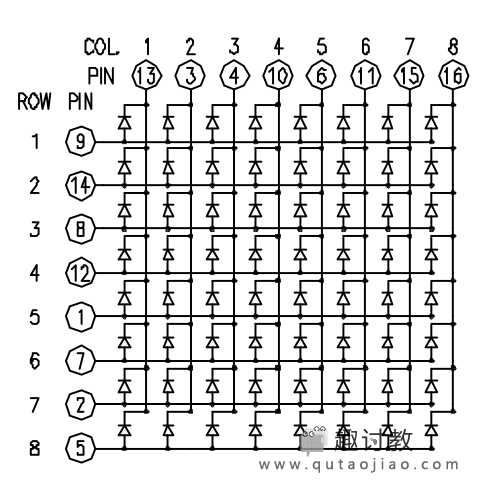
LED灯显示经常打包成一个8x8 LED矩阵,行是共阳极,列是共阴极,或者反过来。这里是一个典型的例子,而它的原理图:
简介
- LED灯显示经常打包成一个8×8 LED矩阵,行是共阳极,列是共阴极,或者反过来。这里是一个典型的例子,而它的原理图:


- 这些是非常有用的显示设备。为了控制矩阵,你把它的行列连接到你的微控制器。列连接到LED的阴极(如图1),所以所有LED灯的列必须是低电平,这样列才能打开。行连接到LED的阳极,所以行必须是高电平来控制一个单独的LED打开。如果行和列都为高电平或者低电平,LED之间会没有电流流过,所以不会打开。
- 为了控制单独的LED灯,你设置列为低电平,而行为高电平。为了控制一行里的多个LED灯,你要设置行为高电平,列也为高电平,然后设置根据要求列低电平或者高电平;一个低电平的列可以打开相应的LED灯,而一个高电平的列则会关闭LED灯。
注意:如果没有特别说明,通过PinMode命令设置为输出的引脚要设置为低电平。 - 虽然有预先制作好的LED矩阵,你也可以用64个LED灯制作一个属于你自己的矩阵。原理图如上面:
- 哪一个微控制器的引脚连接到行和列都没有关系,因为你能在软件里设置这些东西。尽量用一种简单点的方式连接引脚。一个典型的排版如下。
- 这里是一个基于上面原理图的矩阵引脚连接表:
| Matrix pin no. | Row | Column | Arduino pin number |
| 1 | 5 | – | 13 |
| 2 | 7 | – | 12 |
| 3 | – | 2 | 11 |
| 4 | – | 3 | 10 |
| 5 | 8 | – | 16 (analog pin 2) |
| 6 | – | 5 | 17 (analog pin 3) |
| 7 | 6 | – | 18 (analog pin 4) |
| 8 | 3 | – | 19 (analog pin 5) |
| 9 | 1 | – | 2 |
| 10 | – | 4 | 3 |
| 11 | – | 6 | 4 |
| 12 | 4 | – | 5 |
| 13 | – | 1 | 6 |
| 14 | 2 | – | 7 |
| 15 | – | 7 | 8 |
| 16 | – | 8 | 9 |
硬件要求
- Arduino or Genuino开发板
- 8 x 8 LED 矩阵
- 2 10k Ω电位计
- 连接线
- 面包板
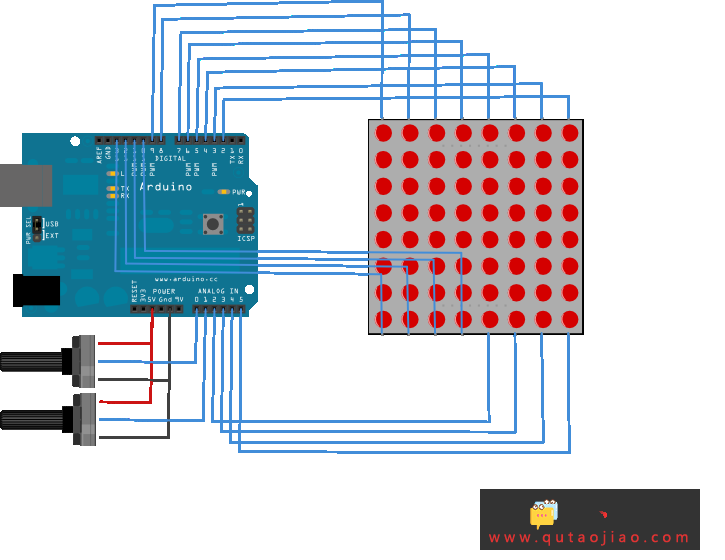
电路
- 矩阵的16个引脚连接到Arduino或者Genuino开发板的16个引脚。4个模拟引脚被当作数字输入引脚16-19。引脚的顺序按代码里的2组数组来分配。
- 两个电位计,连接到模拟引脚pin0和pin1,控制矩阵的LED行动。

原理图

样例代码
// 2-dimensional array of row pin numbers:
const int row[8] = {
2, 7, 19, 5, 13, 18, 12, 16
};
// 2-dimensional array of column pin numbers:
const int col[8] = {
6, 11, 10, 3, 17, 4, 8, 9
};
// 2-dimensional array of pixels:
int pixels[8][5];
// cursor position:
int x = 5;
int y = 5;
void setup() {
// initialize the I/O pins as outputs
// iterate over the pins:
for (int thisPin = 0; thisPin < 8; thisPin++) {
// initialize the output pins:
pinMode(col[thisPin], OUTPUT);
pinMode(row[thisPin], OUTPUT);
// take the col pins (i.e. the cathodes) high to ensure that
// the LEDS are off:
digitalWrite(col[thisPin], HIGH);
}
// initialize the pixel matrix:
for (int x = 0; x < 8; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < 8; y++) {
pixels[x][y] = HIGH;
}
}
}
void loop() {
// read input:
readSensors();
// draw the screen:
refreshScreen();
}
void readSensors() {
// turn off the last position:
pixels[x][y] = HIGH;
// read the sensors for X and Y values:
x = 7 - map(analogRead(A0), 0, 1023, 0, 7);
y = map(analogRead(A1), 0, 1023, 0, 7);
// set the new pixel position low so that the LED will turn on
// in the next screen refresh:
pixels[x][y] = LOW;
}
void refreshScreen() {
// iterate over the rows (anodes):
for (int thisRow = 0; thisRow < 8; thisRow++) {
// take the row pin (anode) high:
digitalWrite(row[thisRow], HIGH);
// iterate over the cols (cathodes):
for (int thisCol = 0; thisCol < 8; thisCol++) {
// get the state of the current pixel;
int thisPixel = pixels[thisRow][thisCol];
// when the row is HIGH and the col is LOW,
// the LED where they meet turns on:
digitalWrite(col[thisCol], thisPixel);
// turn the pixel off:
if (thisPixel == LOW) {
digitalWrite(col[thisCol], HIGH);
}
}
// take the row pin low to turn off the whole row:
digitalWrite(row[thisRow], LOW);
}
}











請問可以用圖像化編輯(像scratch)的講一次嗎??謝謝!